The Hallmarks of Good Governance in Academy Trusts – Part 4
A series of posts examining what good governance in an academy trust looks like and how boards can create a framework to deliver their core purpose and properly discharge their duties. In part 3 we looked at Stewardship of Finance and Resources. In this final part 4 we examine..
How to get governance right from the outset
The Department of Education’s view is that effective governance requires the following key ingredients:
- The right people with the necessary skills, time and commitment, and sufficient diversity of perspectives to ensure internal challenge, all actively contributing in line with clearly defined roles and responsibilities under an effective chair and an explicit code of conduct, and with active succession planning
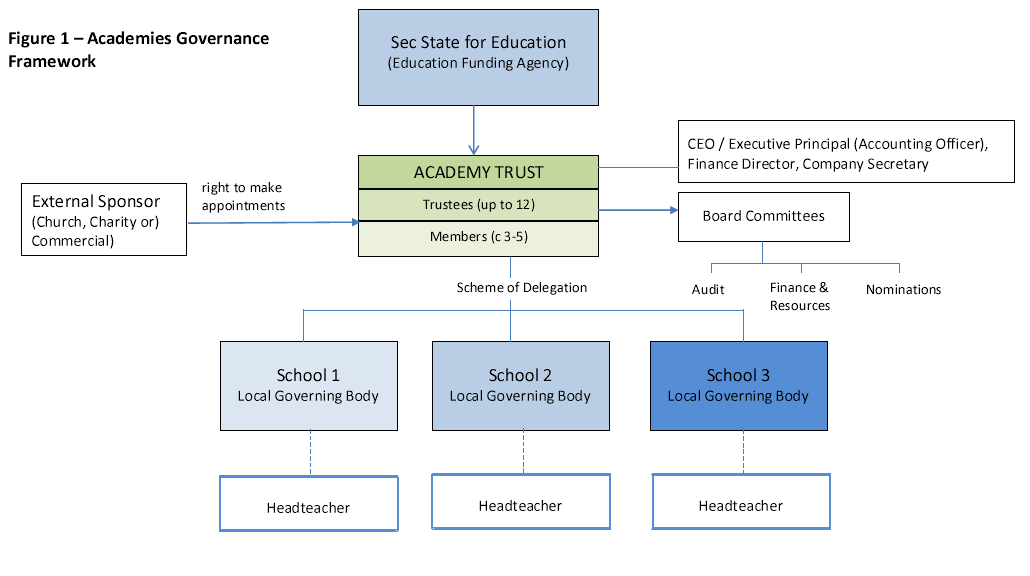
- Clear governance structures and documentation with tightly defined remits, particularly in relation to functions delegated to committees or other bodies
- Clear separation between the strategic and operational in terms of the role of the board and the school management
- A positive relationship between the board and its school management enabling robust constructive challenge on the basis of a good understanding of objective data, particularly on pupil progress, staff performance and finances
- The support and advice of an independent and professional company secretary
- Robust processes for financial and business planning and oversight and effective controls for compliance, propriety and value for money
- Processes for regular self-evaluation, review and improvement including; skills audits, training and development plans, and independent external reviews as necessary.
“Governors and trustees are engaged and energetic non-executive leaders who are driven by their core strategic functions of setting the vision, holding the Headteacher to account or results and making sure money is well spent; they sit on boards no bigger than they have to be; are curious about what’s going on in the classroom and aren’t afraid to innovate; they focus ruthlessly on what really matters: raising standards” – Schools Minister, Lord Nash, 2013
Ensuring continuous improvement
Achieving high standards of governance and accountability requires sustained effort and resources – it isn’t easy. With all aspects of good governance, the effectiveness ultimately depends on the skills, knowledge and behaviour of those responsible for operating the system. The board must set the desired values, ensure they are communicated, incentivise the desired behaviours, and sanction inappropriate behaviour. Academy Trust boards can benefit greatly from an external review of their governance structures and/or an independent review of their board’s effectiveness. In response to the growing need for improvements, Elderflower Legal has developed fixed price review packages which can be delivered quickly, confidentially and with the minimum of fuss to help trustees and school leaders get a picture of how they are performing and what areas of practice need to improve. You can find out more about our review packages here.
Final thoughts
One of the difficulties in embedding sound practice is a current lack of clarity about who is responsible in academy trusts for setting up the framework for sound governance and embedding good practice. CEOs and Executive Principals may not be the best people to lead on this – they are tasked with driving the organisation forward and taking measured risks. Similarly Finance Directors and School Business Managers may be too immersed in the day to day operations and short of time to take an overview of governance. The best person to implement your system is trained governance professional, such as an ICSA-qualified chartered secretary. They have the necessary experience and rigorous qualifications beyond financial and legal aspects to make things happen and help you succeed. Chartered secretaries can work for your trust on an outsourced or employed basis, depending on your budget.
A sound system of governance isn’t a ‘nice to have’, an exercise in box-ticking compliance or even a brake on progress: it is an essential foundation stone on which the whole institution is built. Get it right and it can be enabling and empowering: get it wrong and the academy trust’s whole purpose and even its survival may be compromised.
If you have enjoyed these posts, we have compiled the series “The Hallmarks of Good Governance in Academy Trusts” into a FREE downloadable Special Report. The report can be downloaded here.
Mark Johnson is a highly experienced independent solicitor & chartered secretary supporting academy trusts, free schools & other education providers with their governance arrangements, legal and compliance matters. He is an independent member of a MAT audit committee. He offers a cost-effective governance review GovernanceCHECK360™ for academy trusts elderflowerlegal.co.uk.
If you enjoyed reading this series of posts on Good Governance in Academy Trusts and would like to be kept up to date on similar topics like this, then why not sign up to receive our regular newsletter.